SLC34A2-ROS1[G2032R]/BaF3
CBP73192
| I. Introduction | |
| Cell Line Name: | SLC34A2-ROS1[G2032R]/BaF3 |
| Host Cell: | Ba/F3 |
| Stability: | 16 passages (in-house test, that not means the cell line will be instable beyond the passages we tested.) |
| Application: | Anti-proliferation assay and PD assay |
| Freeze Medium: | 90% FBS+10% DMSO |
| Complete Culture Medium: | RPMI-1640+10% FBS |
| Mycoplasma Status: | Negative |
| II. Background | |
|
Approximately 2% of lung tumors harbor ROS1 fusions (Bergethon et al. 2012). Like ALK fusions, ROS1 fusions are more commonly found in light smokers (<10 pack years) and/or never-smokers. ROS1 fusions are also associated with younger age and adenocarcinomas (Bergethon et al. 2012). |
|
| III. Representative Data | |
|
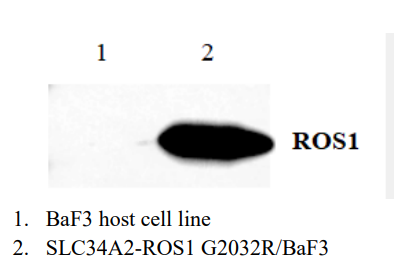
1. WB of SLC34A2-ROS1[G2032R]/BaF3 expression
Figure 1. Protein Expression of ROS1 detected by antibody |
|
|
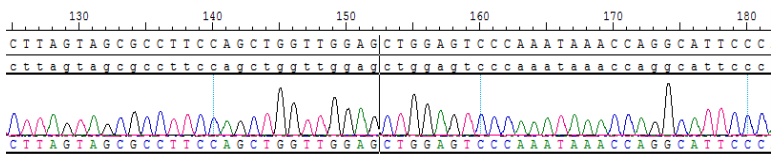
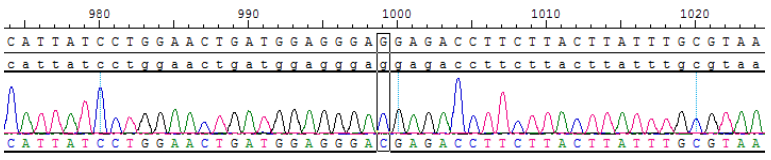
2.Sanger Sequencing of SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion and G2032R mutation
Figure 2. SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion
Figure 3. ROS1 p.G2032R |
|
|
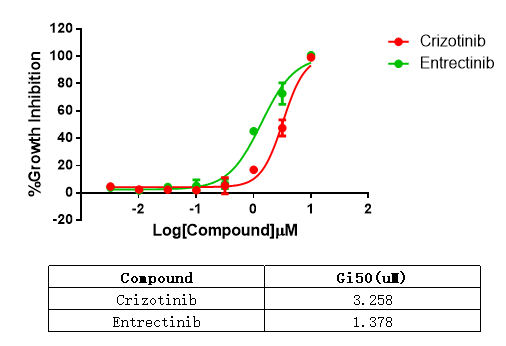
3. Anti-proliferation assay |
|
|
Figure 4. Anti-proliferation assay of two reference compounds on the SLC34A2-ROS1[G2032R]/BaF3 Stable Cell Line. |
|